Trasanction Stroage & Config Team
Introdunction
Achieve the workflow(BatchMoveEndpoint) in AWS and demonstrate the server(SableManagementServer) can be implemented in Native AWS.
PDF: [Proof of Conceop] SableManagementServer BatchMoveEndpoints in NAWS: Design Doc
What I did
- Migrated the BatchMoveEndpoint (BME) workflow to AWS, ensuring full implementation of SableManagementServer (SMS) within the native AWS environment, which reduced 128 maintenance tickets annually.
- Evaluated different AWS services for server deployment, including EC2, ECS, and Step Functions, and analyzed them against our current needs. Ultimately, I opted for Step Functions for implementation and carried out the system design accordingly.
- Decoupled the workflow into 12 modular units, transitioning from Python to Java, and rigorously tested each unit to ensure robust functionality, thereby achieving 99.9% uptime.
- Utilized the AWS Cloud Development Kit (CDK) for a code-first infrastructure approach, configuring a suite of AWS services including Lambda functions, S3, and VPC, which resulted in a 75% reduction in deployment time compared to manual configuration via the AWS Management Console.
- Orchestrated a network of independent AWS Lambda functions into a unified workflow using AWS Step Functions, overcoming the complexity of inter-lambda parameter passing via S3 bucket integration. This architecture enhancement increased process efficiency by 40% and reduced operational costs by 30%.
- Enhanced data agility by implementing parallel operations within AWS Step Functions, enabling efficient data transfer across multiple source and target hosts.
Motivation
The current Server uses architecture which has the limitation on scalability and maintainability. Here are some reasons that are prompting move to AWS.
-
Improved maintainability: Time required to maintain system, software, hardware update manual.
-
Enhanced scalability: The server needs to handle the storgae of data and workflows efficientyly, but current architeture, a cluster of three hosts, has limitation. The inability to replace or modify individual hosts during a failure is a problem.
-
AWS benefits:
- More easy to maintain: don’t need to reply on our own data and infrastructure. Move to AWS allows all infrastructure management to be code-driven, preventing any conflitcts between deployment and maintenance.
- More friendly
- Lower Learning Curve
- Extensive Documentation
Result
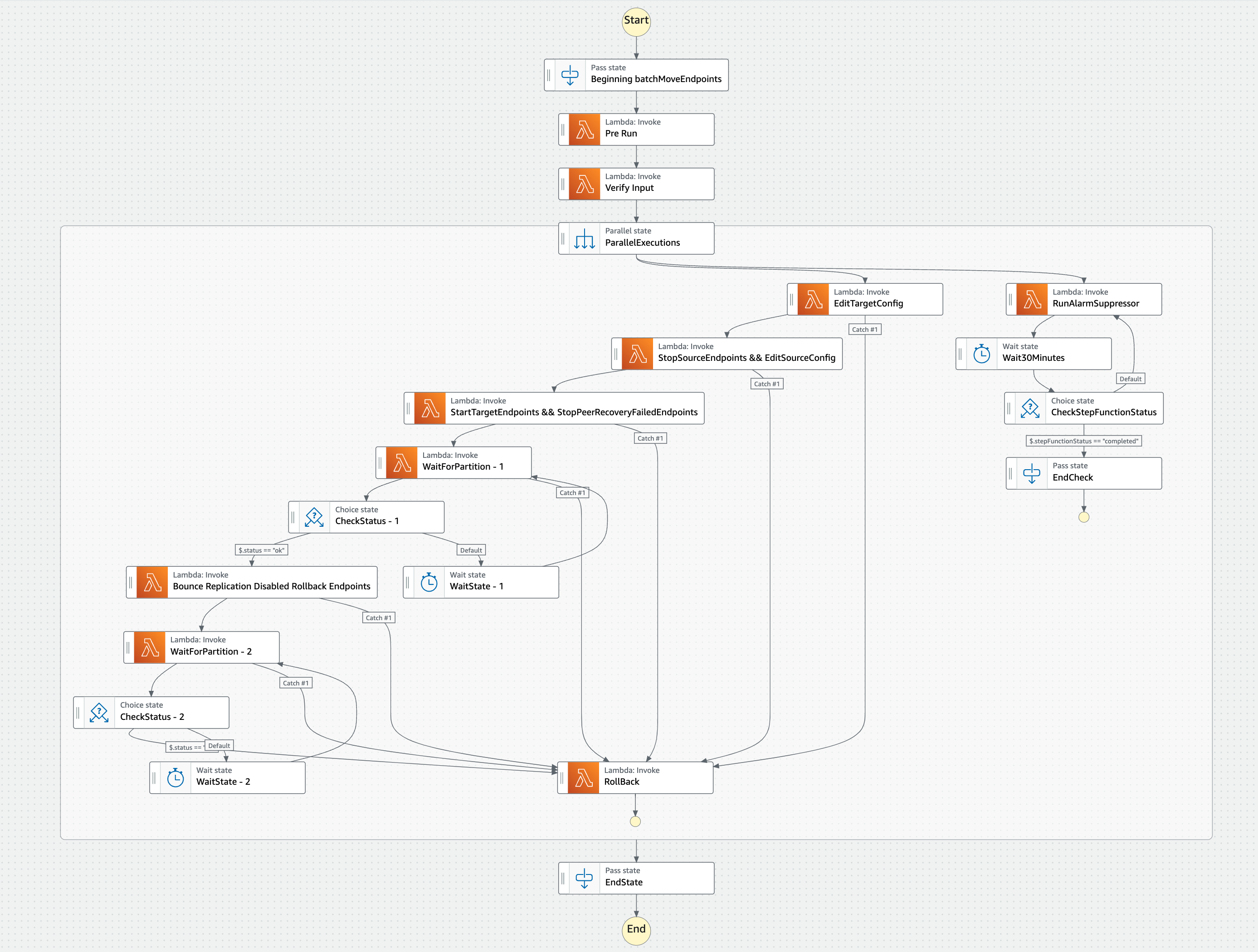
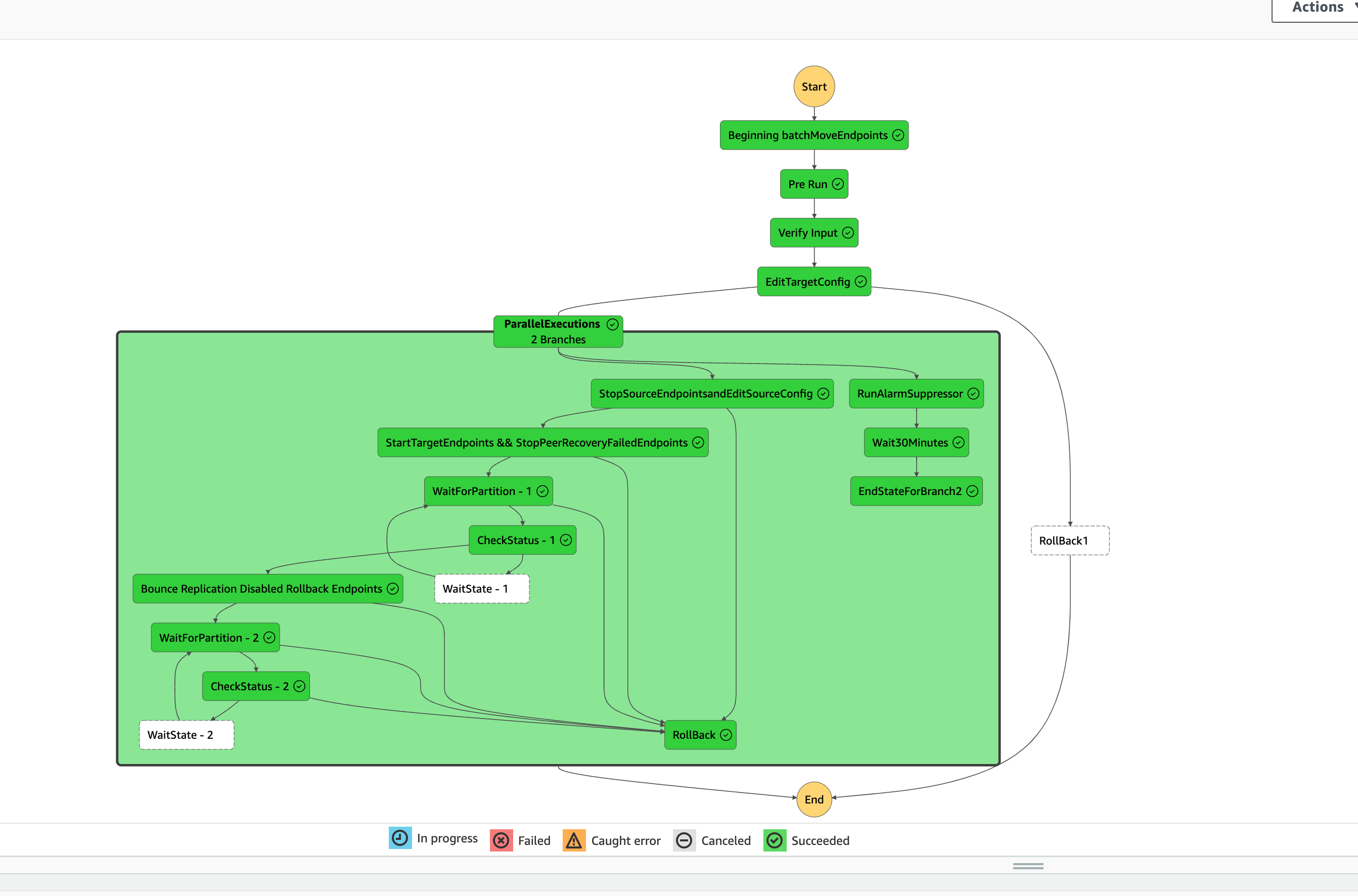
High-level Design
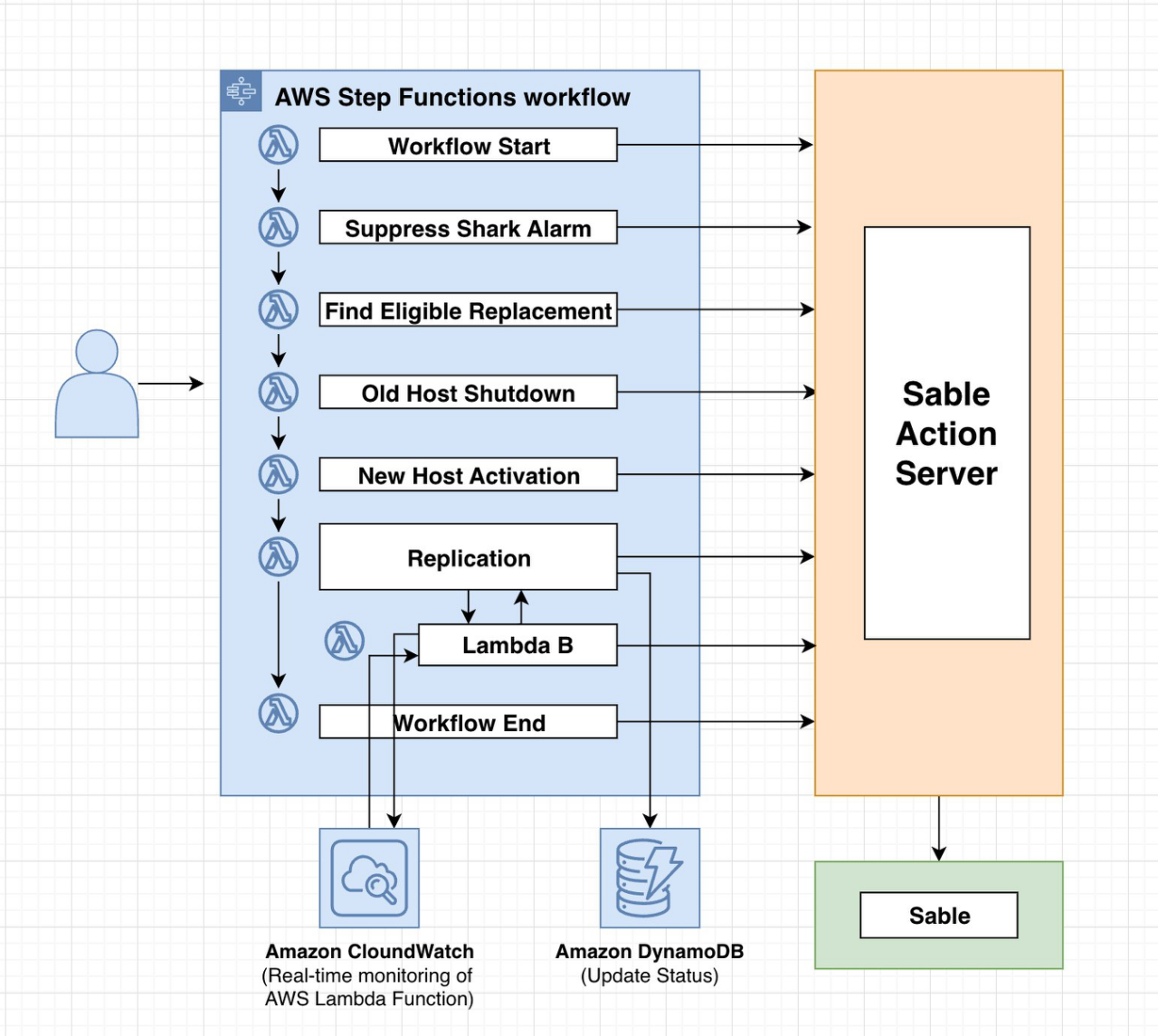
Challengest
-
situation: 项目是将一个平台迁移到AWS环境。这个平台原先运行在Amazon的内部系统“Brazil”上,需要进行改造以适应AWS的架构。特别地,这个迁移涉及到使用步骤函数组合Lambda函数来实现。
-
Task: 需要将原来的平台解耦成多个lambda函数,但lambda函数最多只能运行15分钟。这个任务确保了因为lambda的时间限制而不会导致迁移失败。如果lambda因为达到15分钟的限制而终止,将会引发数据处理不完整,可能导致数据丢失或工作流程中断。
-
Action:
- 将原来逻辑中的重试次数调整为3次。
- 将平台细分成多个小单元,并通过多次测试不同场景,确保每个单元能够在5到15分钟内完成。
- 为了处理边缘情况,在每个单元运行到14分钟时加入逻辑检测。如果已经运行了14分钟,意味着可能由于某些原因无法继续传输数据。此时,我会将当前产生的数据存储到AWS S3桶中,并回滚工作流程,以防止因超时导致的整体失败。
-
Result: 成功解决了Lambda函数的时间限制问题,确保了工作流程的顺利执行。这不仅提高了迁移过程的效率,还保障了数据的安全性和完整性。
Details
decouple的好处
- 增加可维护性:可以单独维护和更新各个部分,提高了整体系统的可靠性和灵活性。
- 增强可靠性: 单个函数出现问题不会影响整个系统,从而提高了整体应用的稳定性。
- 提升灵活性: 独立的函数可以更快地开发和部署,便于快速响应业务需求的变化。
- 优化性能: 函数可以并行运行,提高系统的响应速度和处理能力。
- 降低成本: 按需使用计算资源,只为实际使用的资源付费,避免了资源的闲置浪费。
- 精简测试: 单个函数更容易进行单元测试和集成测试,提高了代码质量。
- 容错和恢复: 出现故障时,只需要重新部署或修复有问题的部分,而不是整个应用。
lambda的时间控制问题 → 在写unit test的测试过程中,我需要严格的保证每一个lambda的运行时间,lambda的运行时间只能在15分钟内,所以我需要尽可能的在每一个功能单元包含多的但是又不能超过15分钟
Step function的好处
- 工作流自动化: 它自动执行工作流中的各个步骤,减少了手动干预的需要。
- 可视化管理: 提供一个直观的界面,让您可以看到工作流的各个步骤和它们的当前状态。
- 灵活的集成: 可以轻松地与其他AWS服务集成,如Lambda、DynamoDB、S3等。
- 按使用付费: 按照工作流的执行次数和状态转换次数付费,无需预先投资。
因为我是通过step function串联了我的lambda,所以lambda之间的参数的传递成为一个难点。因为lambda是可以有input和output的,但只能接受JSON格式。所以这里有一个序列化(Serializtion) 和反序列化(Deserialization)的步骤。
Why Stepfunction rather than EC2?
- 自动扩展和容错:Step Functions 自动处理扩展和容错,确保工作流的执行即使在高负载下也能保持高可用性。相比之下,使用 EC2 实例通常需要手动设置自动扩展策略和容错机制。
- 自动缩放:Step Functions 可以根据工作流执行的数量自动缩放,以适应请求量的变化。这意味着在请求量增加时,Step Functions 能够动态地增加资源来处理更多的工作流,并在负载减少时相应地减少资源。
- 内置容错:Step Functions 通过多个可用区内的冗余部署来提高容错能力。如果一个区域发生故障,Step Functions 可以自动切换到其他区域以维持服务的持续可用性。
- 状态持久性:Step Functions 保持每个工作流的状态,即使在高负载或部分系统故障的情况下,也能确保不丢失状态信息。这有助于在发生故障后快速恢复执行。
- 错误处理和重试策略:Step Functions 允许定义错误处理逻辑和重试策略,这有助于在执行步骤失败时自动进行处理和重试,而无需人工干预。
- 分布式执行:Step Functions 的设计允许工作流的分布式执行,工作流中的各个步骤可以在不同的计算资源上并行或独立运行,从而提高了整体的可用性和效率。
- 持续监控和维护:AWS 持续监控 Step Functions 服务的性能,并自动进行维护更新以确保服务的最佳状态。
- 成本效益:对于事件驱动或间歇性工作负载,Step Functions 可能更加成本效益,因为你只为工作流执行的状态转换付费,而不需要为持续运行的服务器付费。而 EC2 实例则需要按小时计费,不管它们是否处于活动状态。
- 简化的开发和部署:Step Functions 提供了声明式的状态机模型,简化了工作流的定义、部署和管理。这可以加速开发过程,特别是对于复杂的业务逻辑和多步骤工作流。
- 工作流管理:Step Functions 是一种完全托管的服务,专为简化复杂工作流的协调和状态管理而设计。如果你需要编排多个 AWS 服务(如 Lambda、S3、DynamoDB 等)之间的工作流,Step Functions 提供了一个可视化界面和声明式 API 来定义和管理这些步骤。
- 无服务器架构:Step Functions 可以与 AWS Lambda 等无服务器计算服务无缝集成,使你能够构建无需管理服务器的应用程序。这种模式减轻了运维负担,因为 AWS 负责维护底层计算资源。
- 无服务器架构的关键特点包括:
- 事件驱动:大多数无服务器计算平台都是基于事件驱动的,这意味着你的代码会在检测到一个或多个预定义事件时自动执行。
- 按需计算:代码只在需要时运行,你只为实际计算时间付费。当代码不运行时,没有费用产生。
- 管理型服务:底层基础设施由云服务提供商管理。这包括服务器的维护、扩展和更新等任务。
- 自动扩展:应用程序可以根据需要自动扩展到几乎无限的容量,也可以缩减到零。
- 内置高可用性和容错:无服务器平台通常在多个数据中心内部署,以实现高可用性和容错性。
- 无服务器架构的关键特点包括:
- 集成和API支持:Step Functions 提供广泛的 API 支持和与其他 AWS 服务的内置集成,这使得构建和集成跨服务的复杂应用程序变得更加容易。
Why do I plan to use AWS CDK instead of CloudFormation?
AWS CloudFormation and AWS CDK are automation tools provided by AWS for creating and managing cloud environments.
CloudFormation offers a stable, straightforward, and easily understandable way to define and deploy cloud environments, but may become complex and hard to maintain when dealing with complex environments.
On the contrary, CDK allows you to define your cloud environment using regular programming languages such as TypeScript, Python, Java, etc., making code reuse and abstractions simpler, but its learning curve may be steeper, especially for those unfamiliar with programming.
Therefore, if you value the advantages of a programming language, like code reuse and higher-level abstractions, along with using familiar development tools, choosing AWS CDK over CloudFormation makes sense.
How do I make sure the code quality?
- Compile-time check
- Use type-safe parameters and return types to avoid type conversion errors.
- Unit Testing
- Use testing frameworks such as JUnit to automate the tests.
- Check boundary conditions and exceptions.
- Integration test
- Test functions in the broader context of the system to ensure that interactions with other components work as expected.
- Code review
- Check for potential logic errors and suggestions for improvement through code reviews by colleagues.
- Static code analysis
- Use tools such as SonarQube, Checkstyle, PMD, or FindBugs to detect potential issues and bad practices in your code.
- Code coverage analysis
- Use a tool such as Jacoco to analyze code coverage and ensure that the test cases cover all code paths.
- Continuous Integration (CI)
- Automate the above tests in your CI/CD pipeline to ensure that every commit or merge request doesn’t break existing functionality.
- Error handling and logging
- Make sure that your function has an appropriate error handling mechanism.
- Use logging to track the behavior of your functions for easy diagnosis and debugging of problems.